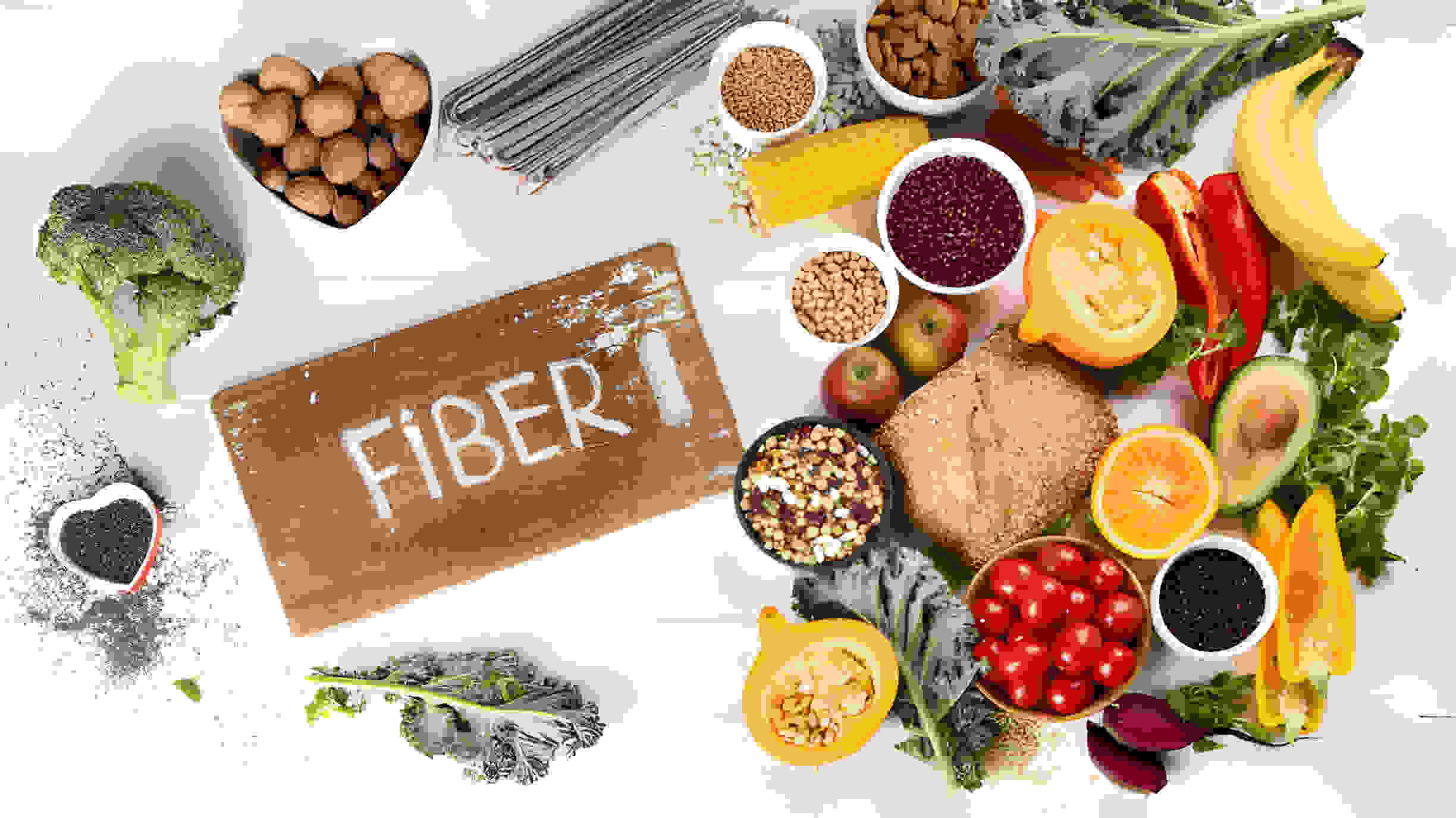
Nothing can give you more peace and prosperity if you have poor health. Optimal health involves maintaining a dynamic physical, mental, and social well-being state. Thus, it emphasizes the importance of proactive measures and mindful approaches to foster overall vitality.
Diabetes is one of the most common health conditions in the world. A report from 2021 suggests that 10.5% of the world’s adult population has diabetes, and half of them are unaware of living with that condition.
Diabetes encompasses a range of health issues, including heart disease, kidney dysfunction, nerve complications, and vision impairments, underscoring the adverse effects this condition can have on overall well-being.
However, including dietary fiber or the best fiber supplement can effectively manage diabetes and improve your well-being. Fiber plays a significant role in fighting diabetes!
In this blog, we shall delve into topics like:
-
What is Fiber? Role in Eliminating Diabetes
-
The Benefits of Fiber: How it Aids Diabetic Patients
-
Fiber-rich Food Items To Include in Your Everyday Diet
-
Quick Tips for Daily Fiber Intake
-
What Type of Fiber Is Good for Diabetes?
Continue reading as we understand more about the role of fiber in treating diabetes in the following sections.
What is Fiber? Role in Eliminating Diabetes
Fiber is the non-digestible component found in plant-based foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, essential for promoting digestive health by adding bulk to stool and facilitating regular bowel movements. Additionally, dietary fiber offers health advantages, including blood sugar control, cholesterol reduction, and promoting a sense of satiety.
Fiber plays a pivotal role in diabetes management by aiding in the gradual absorption of glucose, thereby helping regulate blood sugar levels. Diets rich in fiber have been linked to enhanced insulin sensitivity and improved glycemic control, making them a valuable element in diabetes care.
Why Fiber is Important for Diabetic Patients?
Dietary fiber is essential for individuals with diabetes as it regulates blood sugar levels. The soluble fiber in foods such as oats and legumes significantly slows down glucose absorption and prevents sudden spikes in blood sugar. Moreover, a fiber-rich diet promotes a feeling of fullness, supporting weight management, which is crucial for effective diabetes control.
The Benefits of Fiber: How it Aids Diabetic Patients
Dietary fiber is essential in a healthy diet, with well-established advantages for individuals managing diabetes. Fiber consists of the indigestible parts of plant-based foods, and its incorporation into the diet can offer numerous benefits for those with diabetes.
-
Blood Sugar Regulation:
Soluble fiber in foods like oats, beans, and fruits aids in regulating blood sugar levels by slowing down glucose absorption. This is particularly beneficial for managing postprandial blood glucose spikes in individuals with diabetes.
-
Enhanced Insulin Sensitivity:
Regular fiber intake plays a pivotal role in improving insulin sensitivity, turning the tide in diabetes management. Fiber transforms into the virtuoso conductor, leading to a harmonious response to insulin, ultimately creating a symphony of better glycemic control.
-
Weight Management:
The best fiber supplement weight loss or high-fiber foods are filling and low calories, promoting a sense of fullness and reducing overall calorie intake. This can be advantageous for diabetic individuals aiming for healthy weight management, a crucial aspect of diabetes care.
-
Improved Lipid Profile:
Fiber has positively affected lipid profiles, including reduced LDL cholesterol levels. This is significant for diabetic patients who often face a higher risk of cardiovascular complications, contributing to overall heart health.
-
Stabilizing Blood Pressure:
Certain types of fiber, particularly soluble fiber, have been linked to modest reductions in blood pressure. Maintaining healthy blood pressure is vital for preventing cardiovascular complications in individuals with diabetes.
-
Improved Gut Health:
Fiber promotes a healthy gut microbiota, influencing various aspects of metabolic health. A balanced and diverse gut microbiome is associated with improved glucose metabolism and reduced inflammation, both crucial for diabetic patients.
-
Management of Diabetes-Related Complications:
Beyond blood sugar control, fiber contributes to the prevention or management of diabetes-related complications such as constipation and diverticular disease, shared concerns for those with diabetes.
Fiber-rich Food Items To Include in Your Everyday Diet
Including high-fiber foods in your diet can be beneficial for managing diabetes. Fiber helps regulate blood sugar levels by slowing down the absorption of glucose. Here are some rich sources of high-fiber foods that can be beneficial for individuals with diabetes:
-
Whole Grains: Opt for brown rice, quinoa, barley, and whole wheat over refined grains. These grains are rich in fiber and have a lower glycemic index.
-
Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are excellent sources of fiber. They also provide protein, making them a great option for balancing blood sugar levels.
-
Vegetables: Include leafy greens, broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, and other non-starchy vegetables. They are high in fiber and low in carbohydrates, making them good choices for managing diabetes.
-
Fruits: While fruits contain natural sugars, they also provide fiber. Choose fruits with a lower glycemic index, such as berries, apples, and pears, and consume them in moderation.
-
Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, chia seeds, flaxseeds, and walnuts are rich in fiber and healthy fats. They can be great additions to salads and yogurt or consumed as snacks.
-
Oats: Oats are a good source of soluble fiber, which can help lower cholesterol levels and regulate blood sugar. Opt for steel-cut or rolled oats instead of instant oats for higher fiber content.
-
Sweet Potatoes: Sweet potatoes are a nutritious and fiber-rich alternative to regular potatoes. They have a lower glycemic index and provide essential nutrients.
-
Berries: Berries such as strawberries, blueberries, raspberries, and blackberries are not only rich in fiber but also packed with antioxidants that can benefit overall health.
-
Brans: Wheat bran, rice bran, and oat bran are concentrated sources of fiber. Adding these to your diet, such as in cereals or as toppings, can contribute to your daily fiber intake.
-
High-Fiber Snacks: Choose snacks high in fiber, such as air-popped popcorn, vegetable sticks with hummus, or whole fruits. They are also considered the best fiber supplement for weight loss.
Quick Tips for Daily Fiber Intake
Ensuring an adequate daily dietary fiber intake is vital for individuals managing diabetes, as it plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels and promoting overall well-being. According to Health.gov, women between 19 and 30 should aim for at least 28 grams of fiber daily, while men should target 33.6 grams. After 30, women and men should take 25 grams and 28 grams, respectively.
Incorporating fiber-rich foods like whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes into the diet can help slow the absorption of sugar, improving insulin sensitivity and contributing to glycemic control. Moreover, the feeling of fullness induced by fiber can support weight management—a critical aspect of diabetes care.
Those with diabetes need to prioritize high-fiber options within their meals, as these choices benefit blood glucose levels and enhance heart health and digestive function. Nevertheless, individuals should consult their healthcare providers to determine a personalized and suitable fiber intake based on their specific health conditions.
What Type of Fiber Is Good for Diabetes?
Soluble fiber is advantageous for diabetes management, as it is present in oats, beans, lentils, fruits, and vegetables. This type of fiber dissolves in water to create a gel-like substance, aiding in the gradual absorption of glucose and promoting better blood sugar control. Incorporating diverse soluble fiber sources into the diet can enhance glycemic management for individuals with diabetes.
Takeaway:
-
Nearly 10.5% of the world’s population suffers from diabetes, and fiber is an excellent option to control blood sugar and cholesterol.
-
Men above 30 should take 28 grams of fiber, while women should take 25 grams daily.
-
Soluble fiber is best for diabetes management and also aids different aspects of your health, keeping you healthy in the long run.