Introduction
“The Essential Guide to Laptop Hard Disk Upgrades” is a comprehensive resource designed to empower users with the knowledge and skills necessary to upgrade their laptop’s hard disk drive (HDD) or solid-state drive (SSD). Whether you’re seeking increased storage capacity, faster performance, or enhanced reliability, this guide provides step-by-step instructions, practical tips, and troubleshooting advice to ensure a successful upgrade experience.
From selecting the right replacement drive to transferring data and optimizing performance, this indispensable handbook equips you with the tools and know-how to breathe new life into your laptop’s storage capabilities. Whether you’re a novice or an experienced user, embark on your upgrade journey with confidence using “The Essential Guide to Laptop Hard Disk Upgrades” as your trusted companion.
Understanding Laptop Hard Disks
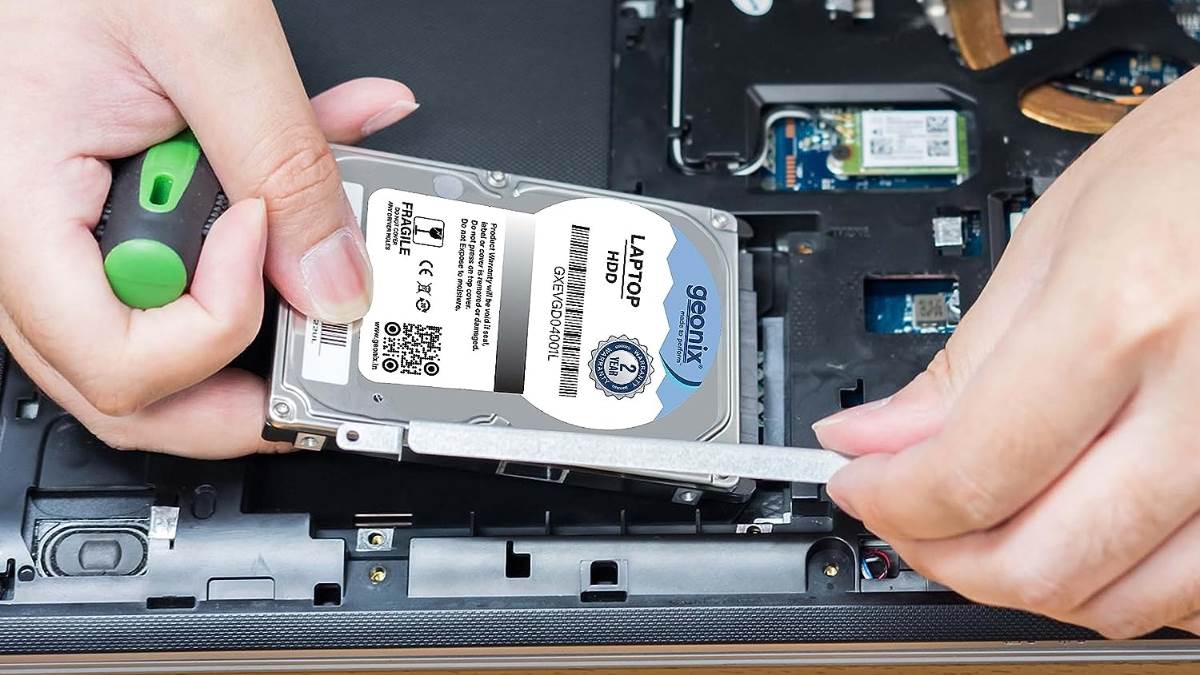
Laptop hard disks, also known as hard disk drives (HDDs) or solid-state drives (SSDs), are essential components responsible for storing and retrieving data on your laptop.
Hard Disk Drive (HDD):
-
HDDs are traditional storage devices that use spinning magnetic disks (platters) to store data.
-
Data is read from and written to these disks using a mechanical arm with a read/write head.
-
They offer relatively large storage capacities at a lower cost per gigabyte compared to SSDs.
-
However, they are slower in terms of data access and transfer speeds due to mechanical components.
Solid-State Drive (SSD):
-
SSDs use flash memory technology to store data electronically, with no moving parts.
-
They offer significantly faster data access and transfer speeds compared to HDDs.
-
SSDs are more resistant to physical shocks and consume less power, making them ideal for laptops.
-
While typically more expensive per gigabyte than HDDs, SSD prices have been decreasing over time.
Storage Capacity:
-
The storage capacity of a laptop hard disk determines how much data it can hold
-
SSD capacities have also been increasing and are available in capacities ranging from a few hundred gigabytes to multiple terabytes.
Form Factor:
-
Laptop hard disks come in various form factors, with 2.5-inch being the standard size for both HDDs and SSDs in laptops.
-
Some laptops may also support smaller form factors such as M.2 SSDs, which are even faster and more compact.
Interfaces:
-
The interface of a laptop hard disk determines how it connects to the laptop’s motherboard.
-
Common interfaces include SATA (for both HDDs and SSDs) and NVMe (for faster SSDs).
-
The interface affects data transfer speeds and compatibility with the laptop.
Reliability and Lifespan:
-
However, both types of drives can fail over time, so it’s essential to regularly back up important data.
Choosing the Right Laptop Hard Disk
Choosing the right laptop hard disk involves considering several factors to ensure that it meets your specific needs and preferences.
Storage Type:
-
Decide between a traditional Hard Disk Drive (HDD) or a Solid-State Drive (SSD).
-
SSDs provide faster performance, improved durability, and energy efficiency.
Storage Capacity:
-
Determine the amount of storage space you need based on your usage patterns.
-
256GB to 512GB SSDs are usually sufficient for basic tasks like web browsing and document editing.
-
If you require ample storage for multimedia files, gaming, or professional work, consider higher capacities (1TB or more).
Form Factor:
-
Ensure that the hard disk’s form factor is compatible with your laptop’s specifications.
-
Most laptops use the standard 2.5-inch form factor for HDDs and SSDs.
-
Some laptops may support smaller form factors like M.2 SSDs, so check your laptop’s documentation.
Interface:
-
Consider the interface of the hard disk and compatibility with your laptop.
-
SATA is the most common interface for both HDDs and SSDs, offering decent performance and widespread compatibility.
-
If your laptop supports faster interfaces like NVMe, consider investing in an NVMe SSD for improved speed.
Performance:
-
Assess your performance requirements based on your usage habits.
-
SSDs offer faster boot times, application loading, and data transfer speeds compared to HDDs.
-
If speed is a priority, opt for an SSD with higher read/write speeds and lower latency.
Reliability and Warranty:
-
Consider the reliability and warranty of the hard disk, especially if you’re storing critical data.
-
SSDs are generally more reliable due to their lack of moving parts, but both HDDs and SSDs can fail over time.
-
Check the manufacturer’s warranty terms and customer reviews for insights into reliability.
Budget:
-
Set a budget for your hard disk upgrade and balance it with your performance and capacity requirements.
-
SSD prices have become more competitive, but they are still generally more expensive than HDDs on a per-gigabyte basis.
-
Consider the long-term benefits of investing in an SSD for improved performance and durability.
Tips for optimizing the performance of the new laptop hard disk
Optimizing the performance of your new laptop hard disk, whether it’s an HDD or SSD, can enhance your overall computing experience.
Update Device Drivers and Firmware:
Ensure that your laptop’s device drivers and firmware are up to date, especially those related to storage controllers and the hard disk.
Enable TRIM (For SSDs):
If you’re using an SSD, make sure that TRIM is enabled in your operating system. TRIM helps maintain the performance of SSDs over time by efficiently managing unused data blocks and improving write performance.
Use the Latest Operating System:
Running the latest version of your operating system can provide performance optimizations and compatibility improvements for modern hardware, including your new hard disk.
Enable AHCI Mode (For SATA SSDs):
If your laptop supports it, ensure that the Advanced Host Controller Interface (AHCI) mode is enabled in the BIOS or UEFI settings. AHCI provides enhanced features and performance benefits for SATA SSDs.
Optimize Power Settings:
Adjust your laptop’s power settings to balance performance and energy efficiency. Choose power plans that prioritize performance when plugged in and battery life when on battery power.
Enable Disk Defragmentation (For HDDs):
If you’re using an HDD, regularly defragment the disk to optimize file placement and improve read/write performance. Most modern operating systems have built-in disk defragmentation utilities.
Minimize Background Processes:
Reduce the number of unnecessary background processes and startup programs to free up system resources and improve overall responsiveness.
Regularly Update Software and Drivers:
Keep your software applications, antivirus programs, and device drivers up to date to ensure optimal compatibility and performance with your new hard disk.
Avoid Overfilling the Disk:
Maintain adequate free space on your hard disk to prevent performance degradation, especially for SSDs. Avoid filling the disk to its maximum capacity, as this can affect write performance and longevity.
Backup Regularly:
Implement a regular backup strategy to protect your data and ensure that you can recover important files in case of hardware failure or data corruption.
Conclusion
In conclusion, optimizing the performance of your new laptop hard disk is essential for maximizing its efficiency, longevity, and overall computing experience. By following the tips outlined in this guide, you can ensure that your hard disk operates at its best, whether it’s a traditional Hard Disk Drive (HDD) or a modern Solid-State Drive (SSD).
Updating device drivers and firmware, enabling features like TRIM and AHCI (for SSDs), and optimizing power settings are crucial steps to enhance performance and compatibility. Additionally, regular maintenance tasks such as disk defragmentation (for HDDs) and minimizing background processes help keep your system running smoothly.
It’s also important to avoid overfilling the disk, regularly update software and drivers, and implement a reliable backup strategy to safeguard your data and protect against hardware failures.
By incorporating these best practices into your routine, you can optimize the performance and reliability of your new laptop hard disk, ensuring that it meets your needs for storage, speed, and efficiency both now and in the future.